
Technology’s Role in Mitigating Railway Incidents
Written by Shahar Hania, Founder and CEO, Rail Vision
Between 2013 and 2022, more than 12,000 incidents occurred on the nation’s 140,000 miles of track. Though the railway industry has accurately asserted significant safety improvements over the past decade, and though the incident rate (derailments, for example, of about three per day, most often in railyards), might not seem alarming, officials on the federal, state and local levels have voiced concerns about the impacts of such incidents.
Advanced technology offers a potential means to further improve safety. Innovative companies like Rail Vision are developing AI-powered obstacle-detection and classification systems for the railway industry. These systems use advanced electro-optic sensors to alert train operators and railway control centers in real time when a train approaches potential obstacles. The systems can detect objects on and along the right-of-way from up to 1.25 miles away, in all weather and light conditions, providing operators with more than 20 seconds to respond. Furthermore, these systems can be integrated with such technology as PTC to automatically apply brakes when an obstacle is detected, even without a engineer’s intervention.
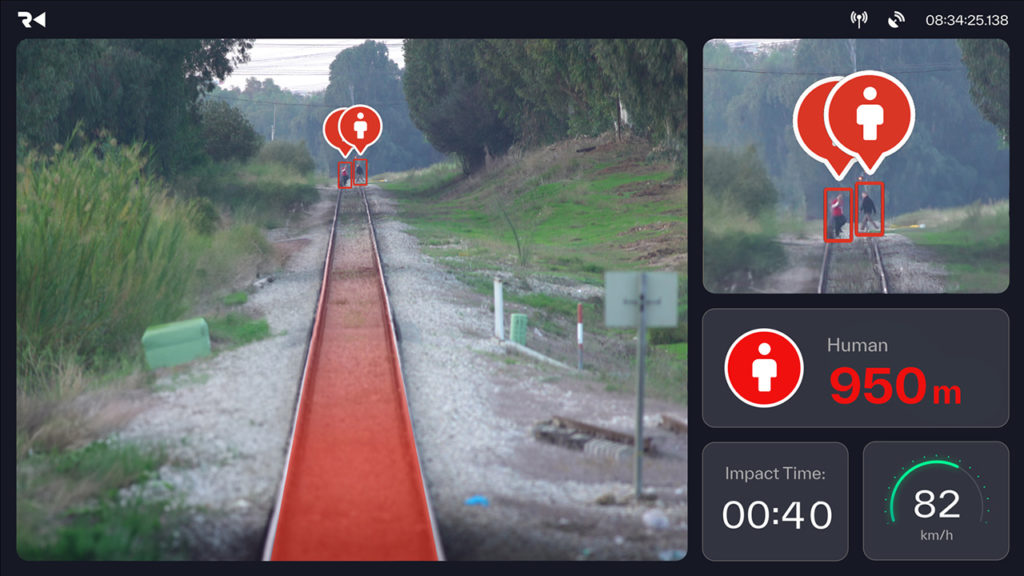
For example, our Main Line System combines sensitive imaging sensors with AI and deep learning technologies to detect and classify obstacles on and near the tracks within a predefined area. It then generates real-time visual and acoustic alerts for both the engineer and the operator’s command-and-control center. The data collected and analyzed provides the basis for additional features, including image-based navigation, predictive maintenance and GIS mapping.
Our Big Data Service enables customized analysis of railway infrastructure and surrounding ecosystems. The Rail Vision system, mounted on the locomotive, collects data that is then evaluated and transferred to the Rail Vision cloud for further analysis and production of reports tailored to customer requests. It uses landmarks to define train position. Where required, the module issues potential infrastructure deficiency alerts. Specific areas can be defined where the Rail Vision system carries out digital GIS mapping, allowing ongoing infrastructure inspection, environmental trend analysis and Image Based (autonomous) Navigation. Generated reports support predictive infrastructure maintenance while enhancing railway safety, resource planning and quality assurance. Data is secured at all stages—from recording to transmission, storage, and analysis.
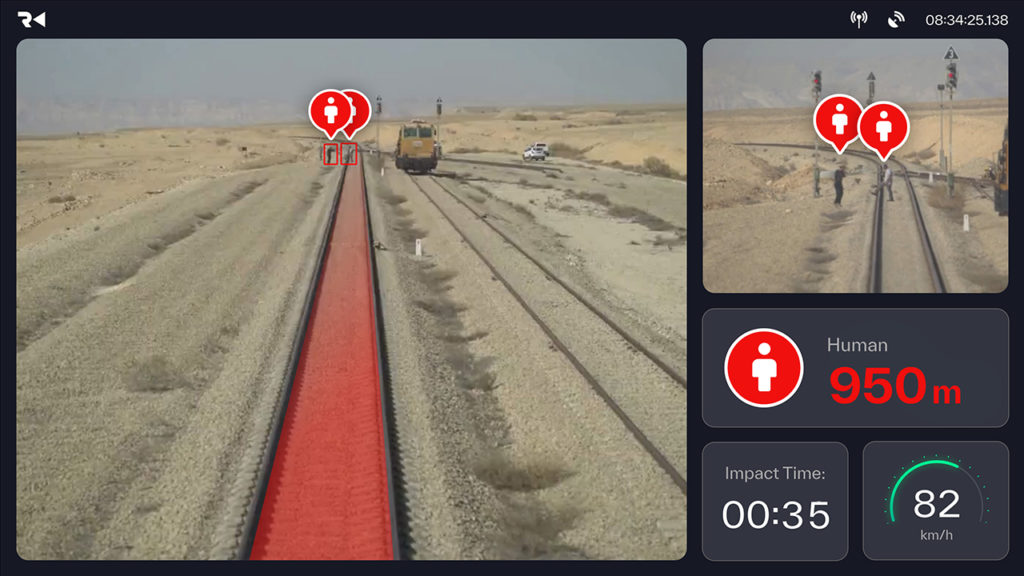
Beyond safety, such technology can also contribute to operational efficiency and cost savings in railway maintenance. Rail Vision’s AI-powered systems monitor tracks to detect workflow slowdowns, quickly alerting operators when they occur. This gives the operators time to reroute trains or devise alternate plans, thereby minimizing disruption.
With the confluence of technology and an increased focus on safety, the hope is that the incident rate will continue to decrease, ultimately leading to safer, more efficient railways.



