
NREL Releases Open-Source ALTRIOS Decarbonization Modeling Software
Written by William C. Vantuono, Editor-in-Chief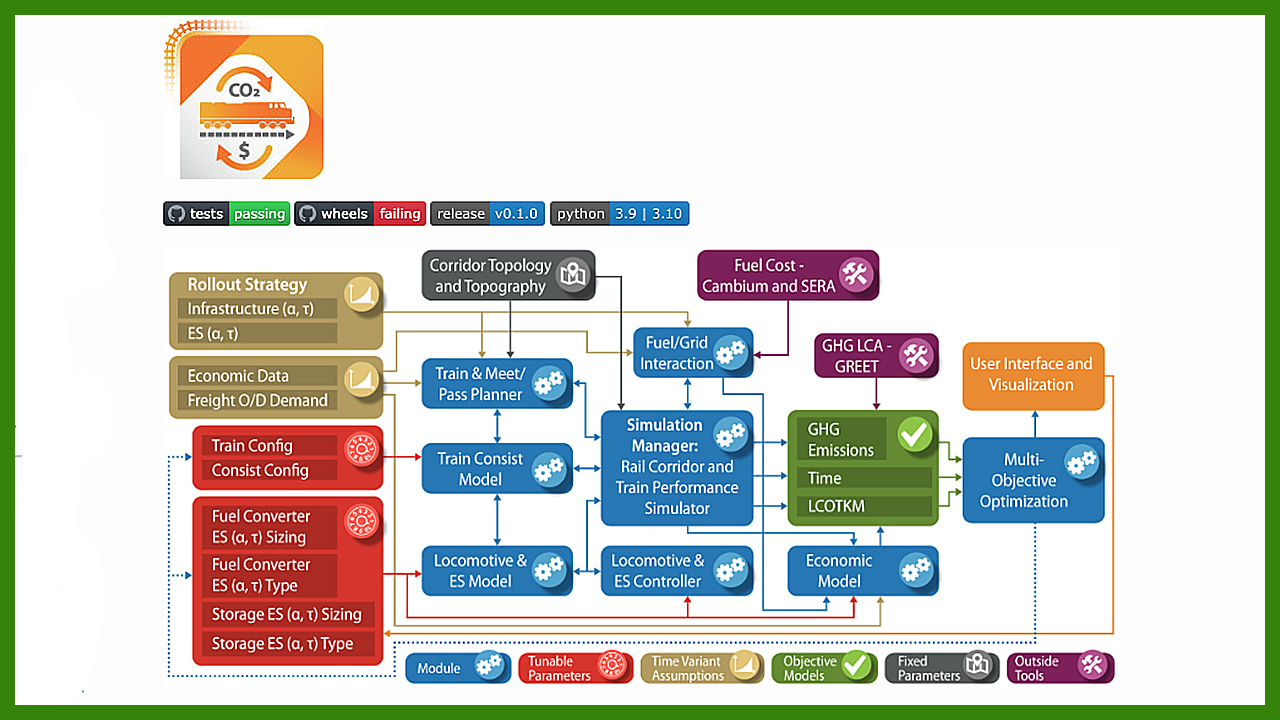
ALTRIOS flow chart. National Renewable Energy Laboratory (NREL) illustration.
The National Renewable Energy Laboratory (NREL) has release ALTRIOS (Advanced Locomotive Technology and Rail Infrastructure Optimization System), described as “the world’s first fully integrated, open-source software designed for exploring deep decarbonization of the rail industry.” ALTRIOS “aims to help freight rail operators transition to clean locomotive technologies and build out associated clean-energy infrastructure in the most cost-effective manner possible.”
NREL scientists developed ALTRIOS jointly with BNSF, Southwest Research Institute (SwRI), the University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign, and the University of Texas at Austin. The U.S. Department of Energy Advanced Research Projects Agency – Energy (ARPA-E) funded the project. NREL says ALTRIOS “simulates real-world rail network operations over the course of decades, allowing researchers to evaluate which clean-energy technology adoption strategies can help rail operators achieve decarbonization targets while minimizing operational costs and scheduling impacts.” The platform “generates realistic deployment scenarios grounded in actual locomotive performance—both battery-electric and conventional Tier 4 diesel-electric locomotives.”
ALTRIOS simulations, NREL notes, offers “real-world, multi-decade rail network operation in a single unified model, including energy-impacting aspects of rail operation” that “can assess the rollout of any energy carriers that could contribute to decarbonized rail operations, including battery-electric, hydrogen-fueled, and biotechnologies.” They are:
- Freight demand-driven train scheduling constrained by technology-specific operating requirements.
- Algorithmically generated target speed traces corresponding to sequences of train departure, meet, and pass events to ensure conflict-free operation.
- Train dynamics, including effects of grade, drag, inertia, rolling resistance, and curvature.
- Locomotive powertrain technologies including diesel electric, battery electric, fuel cell, advanced biofuel, and hybrid fuel technologies.
- Operating condition-based locomotive component efficiencies.
- Consist power distribution controls to minimize powertrain-specific energy consumption.
- Locomotive interactions with fueling and charging infrastructure.
- External constraints such as railcar size and weight limitations, authorized speeds, and grade and curve resistance.
- Sensitivity studies and optimization to explore the rollout of locomotive decarbonization technologies.
“To build ALTRIOS, we worked with industry partners to answer a fundamental question: How can we decarbonize freight rail in an economically viable way?” says NREL commercial vehicle electrification researcher and project principal investigator Jason Lustbader. “ALTRIOS was built to simulate a gradual transition to cleaner technologies. Decarbonization won’t happen overnight. So ALTRIOS doesn’t just illustrate near-term decarbonization strategies. It allows us to scale the strategy over time so that, as clean locomotive technologies advance, rail companies can plan to integrate those into their operations and understand the implications for their service. Throughout the project, we’ve been able to pull on strengths from multiple organizations and integrate them into a powerful tool—one that I think offers an exciting way to accelerate freight rail decarbonizationNow, we’re on track to drive down greenhouse gas emissions in cost-effective ways, in ways that make sense operationally, and in support of our long-term national goals.”
BNSF and SwRI operational data was used to validated ALTRIOS. NREL researchers have begun to use the platform to develop “real-world decarbonization strategies.” In its first deployment, Lustbader and NREL’s Chad Baker, who led software development, demonstrated that adding battery-electric locomotives on a BNSF taconite-hauling route (BNSF video below) “could reduce the railway’s greenhouse gas emissions.” Now, Lustbader and Baker are applying the software to a Parallel Systems freight decarbonization project “that aims to develop autonomous, battery-electric, platooned rail vehicles with flexible routes with the goal of potentially shifting freight from trucks to rail. Because rail can move freight up to four times more efficiently than trucks, projects in a similar vein could realize significant emissions reductions.”
“We incorporated physics-based modeling in key powertrain and train dynamics components to strike a good balance between accuracy and computational performance,” adds Baker, “That gives us a greatly expanded predictive capability compared to a purely data-driven approach, while maintaining a very fast run time and simple configuration. It’s also what makes ALTRIOS a tool that can create meaningful conclusions about the right combination of infrastructure and technology investments to create net-zero-emission freight transport.”
“ALTRIOS is an important start to developing additional open-source modeling tools to help the railroad industry assess decarbonization options,” comments Steven Fritz, who leads SwRI’s locomotive exhaust emissions characterization activities. “ARPA-E’s vision, leadership, and funding set the stage for the project’s partners to bring their expertise to bear on this complex challenge. We are proud to have brought SwRI’s specialties in low-carbon fuels, battery-electric locomotive performance assessment, and locomotive propulsion systems and efficiency to ALTRIOS. We hope to see this innovative tool benefit the public, industry and our government partners.”
ALTRIOS, its developers say, can also be applied to the passenger rail space. “There is an opportunity to examine how to deploy new, cost-effective, decarbonized passenger rail projects,” Lustbader. “There is even potential to update the tool’s modeling capabilities to consider equity and environmental justice concerns, including air quality in historically disadvantaged neighborhoods near freight hubs.”


![“This record growth [in fiscal year 2024’s third quarter] is a direct result of our innovative logistic solutions during supply chain disruptions as shippers focus on diversifying their trade lanes,” Port NOLA President and CEO and New Orleans Public Belt (NOPB) CEO Brandy D. Christian said during a May 2 announcement (Port NOLA Photograph)](https://www.railwayage.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/05/portnola-315x168.png)