The Value of Onboard Data for Predictive Maintenance
Written by Josh Lospinoso, CEO and Co-Founder, Shift5
A new survey of critical transportation and military operators found three-quarters of rail leaders reported that their current tooling fails to provide the access and observability needed to conduct predictive maintenance effectively.
The rail industry is the backbone of the supply chain and economy. Its impact is multifaceted, and as such, the rail system is classified as critical infrastructure. In fact, according to the Association of American Railroads (AAR), in 2020, U.S. freight railroads transported more than 25 million carloads of goods, including raw materials, agricultural products, consumer goods and energy resources. Rail plays a critical role in export and global trade, domestic manufacturing, passenger transportation and national defense and security. The reliability, safety and uptime of rail systems and networks are paramount in maintaining a healthy and flowing supply chain.
Commercial rail operators today are innovating their rail systems into an increasingly complex and technologically advanced network. Such innovations improve operational performance and the rail experience at large. At the same time, these new layers of novel technologies can create challenges in tried-and-true maintenance and operations processes—traditional maintenance that methods haven’t kept up with the pace of rapid technology innovation.
The optimism of innovation is bleeding into the promise of better maintenance solutions. In fact, rail leaders are overwhelmingly optimistic about the potential for predictive maintenance. Within the same survey from MeriTalk, during the next 5 years, rail leaders expect predictive maintenance to:
- Improve average travel speed.
- Reduce shop time for maintenance.
- Improve passenger safety.
- Improve customer satisfaction.
To make these aspirations a reality, rail leaders need to look no further than the data generated from their freight and passenger trains.
Aboard locomotives reside numerous components and data buses that generate enormous volumes of data. This onboard data can enable faster, more precise maintenance outcomes—but only if it’s accessible, understandable and actionable.
Today, most rail operators can’t access the full breadth of onboard data. They can’t use it to improve predictive maintenance efforts. Gaining complete observability into onboard data means that owners, operators and maintainers of rail systems can get the insights and context they need to make real-time decisions that help improve the safety and reliability of their freight and passenger trains.
These reasons underpin why Shift5 introduced its Predictive Maintenance Module. This technology uses real-time data analysis to provide valuable insights for efficient maintenance scheduling. This proactive approach helps prevent critical failures and ensures rolling stock safety and performance.
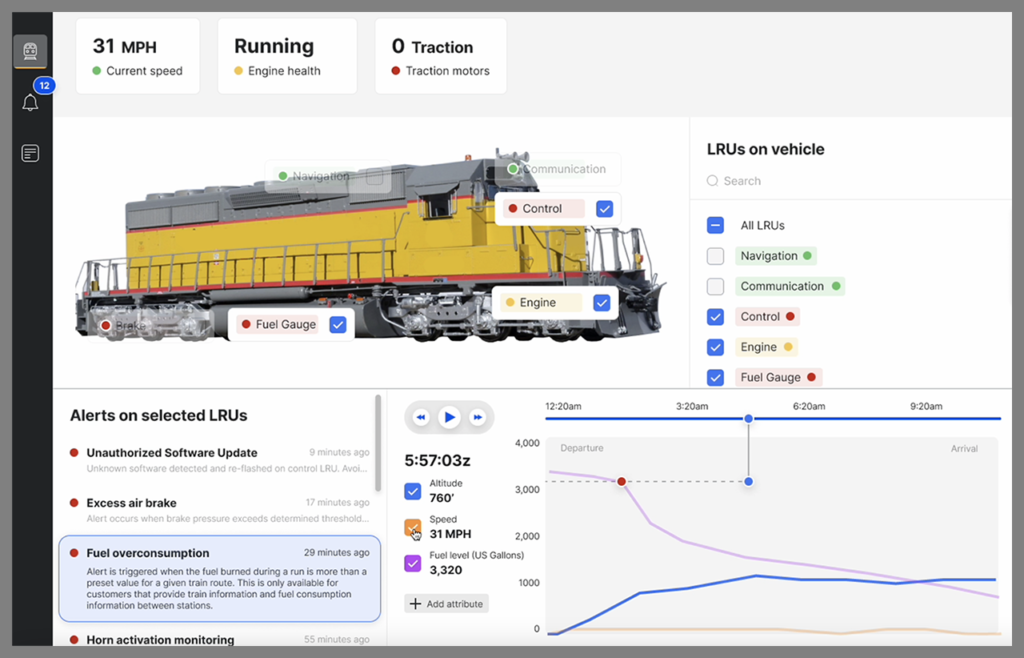
The Shift5 Predictive Maintenance Module is hardware-, bus- and protocol-agnostic. It can perform passive, full-take data capture from components and data buses onboard locomotives—every frame, every bus, every protocol. It can analyze data in real time to provide operators and maintainers with insights to assist in predicting and scheduling maintenance effectively, helping avoid critical failures before they happen.
In addition to its predictive maintenance capabilities, the Predictive Maintenance Module can democratize data and analysis by integrating with customers’ existing systems, tooling and storage, further enhancing team effectiveness and efficiency. The Module provides four key benefits for operators:
- Observability: Access, translate, and store onboard operational data, which can be used to monitor asset performance for patterns or trends that could indicate problems or maintenance issues.
- Readiness: Make better, faster decisions by scheduling maintenance at optimal intervals to reduce downtime, improve availability, optimize resource use and automate early warning indications to mitigate problems before they cause delays.
- Safety: Automate monitoring of system thresholds to forecast and predict equipment failure, perform scheduled maintenance to help reduce the risk of malfunction, and identify and prioritize potential safety hazards.
- Cost savings: Help ensure assets remain in service longer to prevent costly delays and lost revenue, identify and prioritize potential safety hazards to aid in mitigating legal liabilities and fines, and keep assets and components at optimal performance levels to extend their life.
As the rail industry embraces technological innovation, its maintenance practices should benefit as well. Maintenance teams responsible for the reliability, safety and efficiency of their fleets can realize tremendous value when empowered with observability into their onboard data. Predictive maintenance practices can be empowered with data-driven decision-making to enable more accurate and timely maintenance decisions, enhancing operational efficiency.